This post will take a look at what's needed to make an HTTP request in Rust using reqwest and then cross-compile to iOS, Android, and Node.js. Start by cloning the mono-repo created from the Cross Platform Rust: Database Access blog series.
The repo has been updated to include scripts for building each platform independently, as well as together. Run the build script to ensure everything is working properly.
cd cross-platform-rust-database-access
. ./scripts/build.sh
The Android build script needs to be undated in order to build reqwest. Set the TARGET_AR and TARGET_CC environment variables to point to the appropriate toolchain.
TARGET_AR=/Users/logan/.NDK/arm64/bin/aarch64-linux-android-ar
TARGET_CC=/Users/logan/.NDK/arm64/bin/aarch64-linux-android-clang
cargo build --target aarch64-linux-android --release
TARGET_AR=/Users/logan/.NDK/arm/bin/arm-linux-androideabi-ar
TARGET_CC=/Users/logan/.NDK/arm/bin/arm-linux-androideabi-clang
cargo build --target armv7-linux-androideabi --release
TARGET_AR=/Users/logan/.NDK/x86/bin/i686-linux-android-ar
TARGET_CC=/Users/logan/.NDK/x86/bin/i686-linux-android-clang
cargo build --target i686-linux-android --release
Update the rust-core/cargo.toml to include the reqwest dependency. Be sure to remove the rusqlite dependency.
[dependencies]
reqwest = { version = "0.10", default-features = false, features = ["json", "rustls-tls", "blocking"] }
Update rust-core/src/lib.rs with the code below. It makes an HTTP request to get the current IP address and returns the result as a JSON string.
use std::collections::HashMap;
pub fn http_request() -> String {
let client = reqwest::blocking::Client::new();
let response = client.get("https://httpbin.org/ip").send().unwrap();
let resp = response.json::<HashMap<String, String>>().unwrap();
format!("{:#?}", resp)
}
Update the bindings in nodejs/native/src/lib.rs to invoke the http_request method from rust-core.
use neon::prelude::*;
use rust_core::http_request;
fn make_http_request(mut cx: FunctionContext) -> JsResult<JsString> {
let result = http_request();
Ok(cx.string(result))
}
register_module!(mut cx, {
cx.export_function("make_http_request", make_http_request)
});
Also, update the nodejs/lib/index.js to call the new binding.
var addon = require('../native');
console.log(addon.make_http_request());
Build for nodejs and run the node app to see the current IP address.
. ./scripts/build-nodejs.sh
node nodejs/lib/index.js
# {
# "origin": "11.222.33.444",
# }
Update the rust-android bindings in rust-android/src/lib.rs to make the http request.
#![cfg(target_os = "android")]
#![allow(non_snake_case)]
use jni::JNIEnv;
use jni::objects::{JObject};
use jni::sys::{jstring};
use rust_core::http_request;
#[no_mangle]
pub unsafe extern fn Java_com_example_android_MainActivity_makehttprequest(env: JNIEnv, _: JObject) -> jstring {
let http_response = http_request();
let output = env.new_string(http_response.to_owned()).unwrap();
output.into_inner()
}
Update the AndroidManifest.xml to allow the app to access the internet.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.android">
<!-- other settings here -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
</manifest>
Update the MainActivity.kt to invoke the binding.
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
System.loadLibrary("rust_android")
Log.d("rust", makehttprequest())
}
external fun makehttprequest(): String
}
Debug or run the app and see the current IP address in the logs.
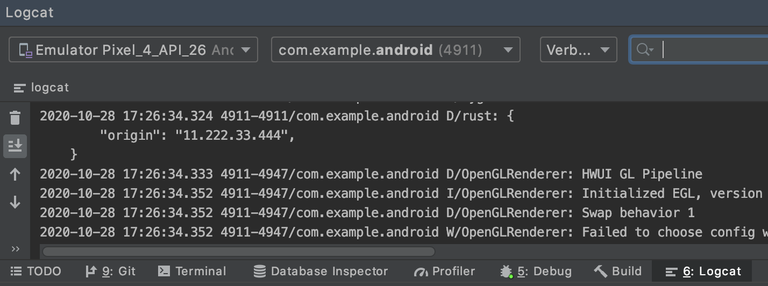
Update the rust-ios bindings in rust-ios/src/lib.rs to make the http request.
use std::os::raw::{c_char};
use std::ffi::{CString};
use rust_core::http_request;
#[no_mangle]
pub extern fn make_http_request() -> *mut c_char {
let response = http_request();
CString::new(response).unwrap().into_raw()
}
#[no_mangle]
pub extern fn make_http_request_free(s: *mut c_char) {
unsafe {
if s.is_null() { return }
CString::from_raw(s)
};
}
Update the ViewController in the iOS app to invoke the binding.
class ViewController: UIViewController {
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// Do any additional setup after loading the view.
let response_cString = make_http_request()
let response = String(cString: response_cString!)
make_http_request_free(UnsafeMutablePointer(mutating: response_cString))
print(response)
}
}
Run or Debug the app and see the current IP address in the logs.
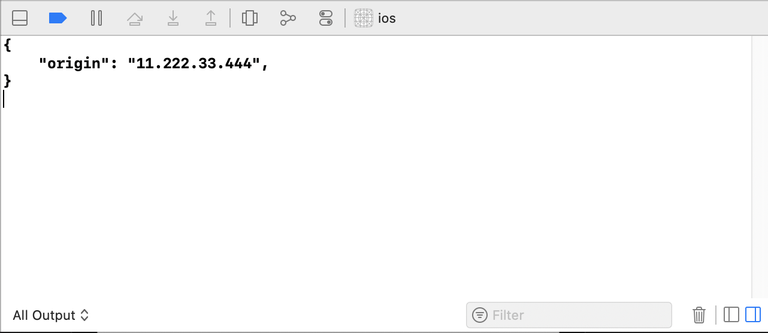
That's it! HTTP requests can be made in Rust and cross-compiled for iOS, Android, and Node.js. An improvement on this could be to use async rather than a blocking HTTP call.